Warning: Undefined array key "lang" in /var/www/bivl2ab-php/html/proyectos.php on line 16
09/09/22
Characterization and optimization of water decontaminating metallic nanofoams supported by geometric representations retrieved with deep learning.

The geometric characteristics of nanostructured porous metallic foams (NMFs) impact their properties, enabling applications in electrocatalysis, energy conversion, and energy storage. The morphology of these three-dimensional (3D) structures is complex, in large part, because of their complicated formation mechanisms. This work presents a computational strategy for geometrically characterizing different NMFs designs. Three types of samples were synthesized using the dynamic hydrogen bubble template electrodeposition method. A set of microscopic confocal images of NMFs was used as training input samples. Herein, a variational autoencoder (VAE) was adjusted under a pretext task, allowing learning embedding descriptors to represent the geometry of microscopic observations. To evaluate the feasibility of using a VAE to assist in the classification of NMFs, a set of machine learning classifiers was implemented to discriminate among the groups of embedded vectors according to their classes. Furthermore, the capacity of the VAE was validated regarding the capability to separate the vectors according to their classes. Explainability mechanisms stand out geometrical features of input images that had major support during the classification task.
See More
April 2020
DeepSARS: Machine learning system for early identification and monitoring of patients at risk of respiratory distress syndrome and acute
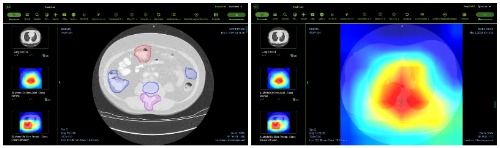
DeepSARS is an automatic deep learning system whose objective is the early identification and follow-up of patients at risk of acute respiratory distress syndrome. This project is developed by the Industrial University of Santander (UIS), the Santander Ophthalmology Foundation (FOSCAL) and the Autonomous University of Bucaramanga (UNAB), with the support of the Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation (MINCIENCIAS).
See More
January 2021
Locomotor pattern quantification for remote diagnosis and monitoring in hard-to-reach areas
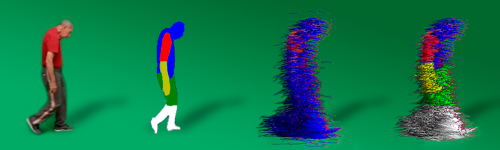
The general objective of this project is to develop a computational strategy for the registration, quantification and representation of gait patterns in semi-controlled environments as support in telerehabilitation assistance processes. This approach allows recording videos of the displacement and particular movements of patients associated with musculoskeletal conditions, supporting the provision of tele-rehabilitation services in vulnerable regions of the country.
See More
January 2021
Prediction of cardiac pathologies using deep learning representations in cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) sequences
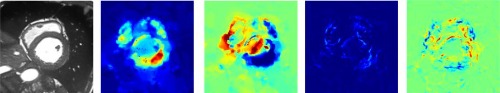
The main objective of the project is to develop a computational method for the characterization and quantification of cardiac patterns in cine-MRI sequences, using deep learning representations, to support the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases. Heart disease is the leading cause of death globally, with more than 17.9 million deaths reported during 2016.
See More
January 2021
Identification of features associated with nuclear pleomorphism in histological images of breast cancer using deep learning algorithms
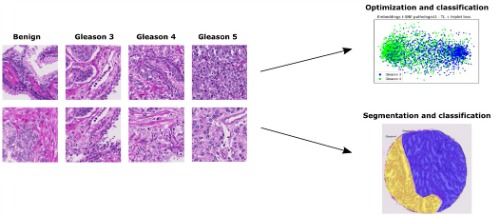
The general objective of this project is to identify and associate visual characteristics learned through supervised and self-supervised learning in deep learning models with nuclear pleomorphism in histological images of breast cancer. It should be noted that breast cancer is one of the most frequent manifestations of cancer that affects women in the world. According to the World Health Organization, the majority (69%) of deaths from this cancer are registered in developing countries.
See More